

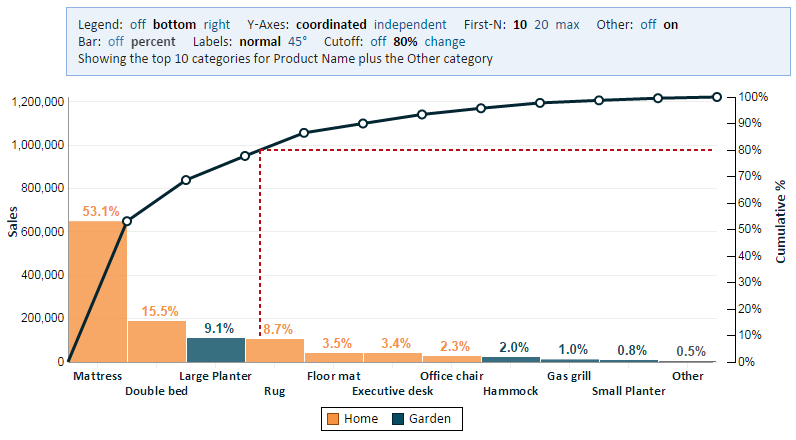
Your problems can be grouped into related categories. You can group the causes of your problems together if they fall under the same categories. This will help you determine if one solution is sufficient to solve multiple problems. process to find the cause of all the problems you are trying to solve. Identify the root causes of your problems. Use a tool such as the 5 Whys The 5 Whys Technique: Origins The 5 Whys steps method was de. Identify the problems your team is facing. This is the problem you are trying to solve in this decision-making process. It can help you prioritize the solutions. These are some steps that will help you understand how it works. The Pareto principle is a way to help you make the right decisions in the problem-solving process. The Pareto principle is useful when there are multiple causes for a problem. framework. The 80-20 Principle is not a law, but an observation. Although it is not always true, the 80-20 and 99-1 distributions are often the most profitable. This is where you can make a lot of money with little effort. within the Lean Six Sigma Six Sigma Definition: Six Sigma is a set of techniques and t. It states that most results are due to a small number of causes or efforts. This is how it fits Fitted values can also be known as fits. The fitted val. The 80/20 Principle is a scientific law that has been proven to be effective in both business and economics. Tiny amounts of energy can go a long way. The Pareto Principle tells us where the most bang for our buck is. It all started with Joseph Juran, who introduced quality control in the 1950s. Juran used the 80-20 Principle to identify the most serious and frequent causes of inferior quality. His clients, who were mostly Japanese, advised him to fix them first. They did. They rose from a devastated nation with no exports to become a stronghold in the 1980s. The Pareto principle (or 80/20 principle) and Lean Six Sigma


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
